It can be challenging to calculate the emissions generated by wearing a t-shirt, as it would depend on a variety of factors such as the materials used to make the t-shirt, the methods used to produce it, and the transportation and disposal of the t-shirt. In general, the emissions generated by the production and use of clothing can be divided into two main categories: direct emissions, which are generated during the production and transportation of the clothing, and indirect emissions, which are generated through the use of energy and other resources in the production process.
To calculate the direct emissions from the production of a t-shirt, you would need to know the materials used to make the t-shirt, the methods used to produce it, and the transportation distances involved. For example, if the t-shirt is made from cotton, you would need to know the amount of water and other resources used in the growing and harvesting of the cotton, as well as the emissions generated by the manufacturing process and the transportation of the t-shirt. More on this later on in this article.
To calculate the indirect emissions from the production of a t-shirt, you would need to consider the energy and other resources used in the production process, such as electricity, fuel, and water. This can be a complex calculation, as it would involve estimating the emissions generated by the various stages of the production process, including spinning, weaving, dyeing, and finishing. Again more details on this later in the article.

Direct emissions are emissions that are generated directly from a specific source, such as the burning of fossil fuels or the production of goods. These emissions are often associated with a specific activity or process and can be measured and quantified based on the number of emissions generated by the activity or process.
Indirect emissions, on the other hand, are emissions that are generated as a result of the use of energy or other resources but are not directly associated with a specific source or activity. These emissions can be more difficult to measure and quantify, as they are often dispersed across a wide range of activities and processes.
One key difference between direct and indirect emissions is the way they are measured and quantified. Direct emissions are typically measured and quantified using data on the emissions generated by a specific source or activity, such as the burning of fossil fuels or the production of goods. Indirect emissions, on the other hand, are typically measured and quantified using data on the energy and resource use in a given process or activity, along with emissions factors that estimate the emissions generated by a given amount of energy or resource use.
Another key difference between direct and indirect emissions is their environmental impact. Direct emissions are often considered to be more significant in terms of their environmental impact, as they are generated directly from a specific source and can be easily measured and quantified. Indirect emissions, on the other hand, are often considered (quite worryingly as this means not as much effort is put into collecting this information) to be less significant in terms of their environmental impact, as they are dispersed across a wide range of activities and processes, and can be more difficult to measure and quantify (and as a result could be significantly larger than current estimates).
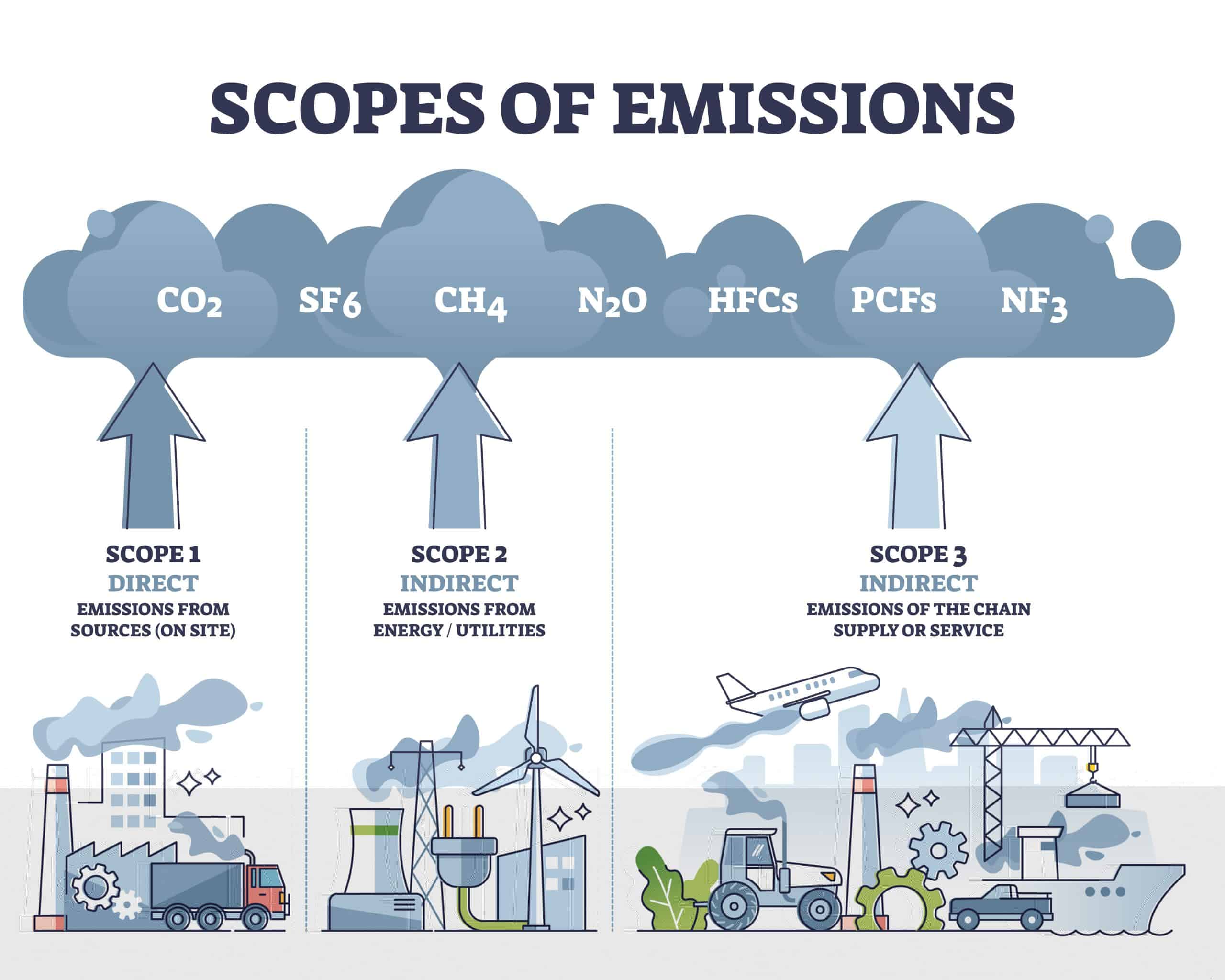
To calculate the direct emissions from the production and transportation of a t-shirt, you would need to know the materials used to make the t-shirt, the methods used to produce it, and the transportation distances involved. For example, if the t-shirt is made from cotton, you would need to know the amount of water and other resources used in the growing and harvesting of the cotton, as well as the emissions generated by the manufacturing process and the transportation of the t-shirt.
Once you have this information, you can use various tools and resources to estimate the direct emissions from the production and transportation of the t-shirt. For example, you could use an emissions calculator to estimate the emissions generated by the transportation of the t-shirt, based on the distance travelled and the mode of transportation used, like the distance calculated in Meet Your Wardrobe. You could also use data on the energy and resource use in the manufacturing process to estimate the emissions generated by the production of the t-shirt, in a similar way to again how Meet Your Wardrobe allows you to calculate your cleaning emissions.
It is important to note that calculating the direct emissions from the production and transportation of a t-shirt is a complex task that involves many assumptions and estimates, and the results may vary depending on the specific data and assumptions used.
To estimate the indirect emissions from the production of a t-shirt, you would need to consider the energy and other resources used in the production process, such as electricity, fuel, and water. This can be a complex calculation, as it would involve estimating the emissions generated by the various stages of the production process, such as spinning, weaving, dyeing, and finishing. Only once you have this data (or estimates) of the indirect emissions from the production of a t-shirt will you be able to make a calculation that takes into account the energy and resource use in the production process. You will also need emissions factors that estimate the emissions generated by a given amount of energy or resource use This is hard to do because data on the emissions generated by different stages of the production process, as well as data on the energy and resource use in the production process is not easy to come by, particularly without being first adjusted by an intermediary.
By using the best available data and tools, you can get a good estimate of the indirect emissions generated by the production of a t-shirt, and use this information to compare the environmental impact of different production methods and materials.
Overall, calculating the emissions generated by wearing a t-shirt is a complex task that would require a detailed understanding of the materials and production processes involved, as well as the transportation and disposal of the t-shirt. It is important to consider the environmental impact of clothing production and consumption and to take steps to reduce our environmental footprint through the use of sustainable materials and production methods.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
Create your free account and begin your sustainability journey.